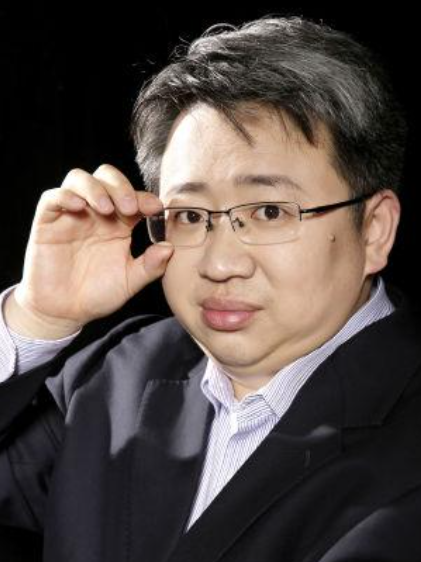
研究领域
植物抗逆营养生理及其分子生物学、植物硅素营养生物学、新型肥料研制与推广应用
教育背景
1979年11月-1983年7月 浙江农业大学土壤农业化学系读本科
1983年9月-1987年7月 南京农业大学土壤农业化学系读硕士生
1987年7月-1990年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院助教
1991年1月-1996年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院讲师
1996年1月-1999年7月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院在职博士生
1997年1月-1999年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院副教授
2000年1月-2003年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院教授
2001年8月-2002年2月 香港浸会大学生物系访问学者
2002年9月-2003年12月 德国霍恩海姆大学(University Hohenheim) 植物营养研究所洪堡学者
2004年1月- 中国农科院植物营养与肥料一级学科杰出人才,教授,博士生导师
2014年 浙江大学教授、博士生导师
学术兼职
农业部植物营养与养分循环重点开放实验室(植物营养与肥料研究室)副主任
中国土壤学会第十、第十一国届理事会“土壤-植物营养专业委员会”副主任
中国植物营养与肥料学会常务理事兼学术委员会主任
中国农业科学院学术委员会委员
中国生态学会理事
本领域SCI 主流刊物“Plant and Soil” 领域编辑(Section Editor)
“Journal of Plant Nutrition” 编委
“Applied and Environmental Soil Science”副主编(Associate Editor)
《植物营养与肥料学报》、《中国生态农业学报》和《干旱区研究》和《石河子大学学报》编委
社会荣誉
1996年 荣获第二届江苏省青年科技标兵称号。
2000年 获第七届中国农学会青年科技奖。
2004年 被评为中国农业科学院植物营养与肥料学科一级岗位杰出人才。
2006年 入选第八批长江学者。
主持973、国家支撑计划、国家基金等课题20余项。
获得省部级科技进步1-3等奖5项。
研究成果
先后共主持973项目课题和子课题各1项,国家支撑计划课题1项和子课题2项,国家自然科学基金8项,国际科学基金2项,北京市自然科学基金1项,国家留学回国基金1项,教育部重大项目培育项目1项,其它省、部级项目5项,横向课题4项。发表论文100余篇,其中在“Plant Physiology”,“New Phytologist” ,“Soil Biology and Biochemistry”,“Plant and Soil”等SCI源刊物上发表论文53篇。
论文:
[1] Li P, Song AL, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Liang YC. 2011. Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant and Soil. (Accepted)(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[2] Fan FL, Yang QB, Li ZJ, Wei D, Cui XA, Liang YC. 2011. Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizers on nitrification in a cold climate soil are linked to the bacterial ammonia oxidizer community. Microbial Ecology. 62:982-990(通讯作者)(影响因子:3.251)
[3] Zhang B, Chu GX, Wei CZ, Ye J, Li ZQ, Liang YC. 2011. The growth and antioxidant defense responses of wheat seedlings to omethoate stress. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 100: 273-279 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.719)
[4] Su YH, Liang YC. 2011. Transport via xylem of atrazine, 2,4-dinitrotoluene, and 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene in tomato and wheat seedlings. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 100: 284-288(影响因子:1.719)
[5] Song AL, Li P, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Nikolic M, Liang YC. 2011. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant and Soil. 344: 319-333. (通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[6] Li ZJ, Xie XY, Zhang SQ, Liang YC. 2011. Wheat growth and photosynthesis as affected by oxytetracycline as a soil contaminant. Pedosphere. 21(2): 244–250(通讯作者)
[7] Sun WC, Zhang J, Fan QH, Xue GF, Li ZJ, Liang YC 2010. Silicon-enhanced resistance to rice blast is attributed to silicon-mediated defence resistance and its role as physical barrier. European Journal of Plant Pathology. 128:39-49 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.931)
[8] Ge GF, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Chu GX, Hou ZA, Liang YC. 2010. Soil biological activity and their seasonal variations in response to long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Plant and Soil. 326:31–44(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[9] Liang YC, Zhu Y-G, Smith FA, Lambers H. 2010. Soil-plant interactions and sustainability of eco-agriculture in arid region: a crucially important topic to address. Plant and Soil. 326:1–2(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[10] Wakelin SA, Chu GX, Lardner R, Liang YC, McLaughlin MJ. 2009. A single application of Cu to field soil has long-term effects on bacterial community structure, diversity, and soil processes. Pedobiologia 53:149-158 (影响因子:2.414)
[11] Wakelin SA, Chu GX, Broos K, Clarke KR, Liang YC, McLaughlin MJ. 2010. Structural and functional response of soil microbiota across a Cu gradient are moderated by addition of plant substrate. Biology and Fertility of Soils 46:333-342 (影响因子:1.757)
[12] Song AL, Li ZJ, Zhang J, Xue GF, Fan FL, Liang YC. 2009. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 172:74-83 (通讯作者)(影响因子:4.144)
[13] Zhang J, Sun WC, Li ZJ, Liang YC, Song AL. 2009. Cadmium fate and tolerance in rice cultivars. Agronomy for Sustainable Development. 29: 483-490 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.65)
[14] Chen WP, Hou ZA, Wu LS, Liang YC, Wei CZ. 2009. Effects of salinity and nitrogen on cotton growth in arid environment. Plant and Soil. 326:61–73(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[15] Guo B, Liang YC, Li ZJ and Han FX, 2009. Phosphorus adsorption and bio-availability in a paddy soil amended with pig manure compost and decaying rice straw. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis. 40: 2185-2199(通讯作者)(影响因子:0.357)
[16] Ma YB, Li JM, Li XY, Tang X, Liang YC, Huang SM, Wang BR, Liu H, Yang XY. 2009. Phosphorus accumulation and depletion in soils in wheat-maize cropping systems: modeling and validation. Field Crops Research. 110:207-212 (影响因子:2.336)
[17] Guo B, Liang YC, Zhu YG. 2009. Does salicylic acid regulate antioxidant defense system, cell death and cadmium uptake and partitioning to acquire cadmium tolerance in rice subjected to cadmium stress? Journal of Plant Physiology, 166: 20-31 (通讯作者)(影响因子:2.5)
[18] Su YH, Zhu YG and Liang YC. 2009. Interactions of mixed organic contaminants in uptake by rice seedlings, Chemosphere, 74: 890-895(通讯作者)(影响因子:3.253)
[19] Ge GF, Li ZJ, Zhang J, Wang LG, Xu MG, Zhang JB, Xie XL, Wang JK, Liang YC. 2009. Geographical and climatic differences in long-term effect of organic and inorganic amendments on soil enzymatic activities and respiration in field experimental stations of China. Ecological Complexity. 6: 421-431(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.03)
[20] Zhang J, Li ZJ, Ge GF, Liang YC, Wu LS. 2009. Impacts of soil organic matter, pH and exogenous copper on sorption behavior of norfloxacin in three soils. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 21: 632–640(通讯作者)(影响因子:1.414)
[21] Wang LG, Liang YC, Jiang X. 2008. Analysis of eight organophosphorus pesticide residues in fresh vegetables retailed in agricultural product markets of Nanjing, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81(4):377-382(影响因子:0.609)
免责声明:本网站所刊登的文章、图片版权均归原作者所有,不代表本公司观点,若有疑义,请与智库联系处理。
政商智库网隶属于北京正商方略经济咨询中心是一家独立的政策研究与咨询机构。广泛联络国内外政府领袖、经济学家、诺贝尔奖学者等,举办国际峰会论坛、组织技术交流、行业研讨会及参访,为社会各界提供智力支持。联系电话:13810102624(王老师)
主要业务领域有:战略咨询、公关服务、承接政府和企业委托、邀请专家出席论坛会议授课等。
全部服务领域


研究领域
植物抗逆营养生理及其分子生物学、植物硅素营养生物学、新型肥料研制与推广应用
教育背景
1979年11月-1983年7月 浙江农业大学土壤农业化学系读本科
1983年9月-1987年7月 南京农业大学土壤农业化学系读硕士生
1987年7月-1990年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院助教
1991年1月-1996年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院讲师
1996年1月-1999年7月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院在职博士生
1997年1月-1999年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院副教授
2000年1月-2003年12月 南京农业大学资源与环境学院教授
2001年8月-2002年2月 香港浸会大学生物系访问学者
2002年9月-2003年12月 德国霍恩海姆大学(University Hohenheim) 植物营养研究所洪堡学者
2004年1月- 中国农科院植物营养与肥料一级学科杰出人才,教授,博士生导师
2014年 浙江大学教授、博士生导师
学术兼职
农业部植物营养与养分循环重点开放实验室(植物营养与肥料研究室)副主任
中国土壤学会第十、第十一国届理事会“土壤-植物营养专业委员会”副主任
中国植物营养与肥料学会常务理事兼学术委员会主任
中国农业科学院学术委员会委员
中国生态学会理事
本领域SCI 主流刊物“Plant and Soil” 领域编辑(Section Editor)
“Journal of Plant Nutrition” 编委
“Applied and Environmental Soil Science”副主编(Associate Editor)
《植物营养与肥料学报》、《中国生态农业学报》和《干旱区研究》和《石河子大学学报》编委
社会荣誉
1996年 荣获第二届江苏省青年科技标兵称号。
2000年 获第七届中国农学会青年科技奖。
2004年 被评为中国农业科学院植物营养与肥料学科一级岗位杰出人才。
2006年 入选第八批长江学者。
主持973、国家支撑计划、国家基金等课题20余项。
获得省部级科技进步1-3等奖5项。
研究成果
先后共主持973项目课题和子课题各1项,国家支撑计划课题1项和子课题2项,国家自然科学基金8项,国际科学基金2项,北京市自然科学基金1项,国家留学回国基金1项,教育部重大项目培育项目1项,其它省、部级项目5项,横向课题4项。发表论文100余篇,其中在“Plant Physiology”,“New Phytologist” ,“Soil Biology and Biochemistry”,“Plant and Soil”等SCI源刊物上发表论文53篇。
论文:
[1] Li P, Song AL, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Liang YC. 2011. Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant and Soil. (Accepted)(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[2] Fan FL, Yang QB, Li ZJ, Wei D, Cui XA, Liang YC. 2011. Impacts of organic and inorganic fertilizers on nitrification in a cold climate soil are linked to the bacterial ammonia oxidizer community. Microbial Ecology. 62:982-990(通讯作者)(影响因子:3.251)
[3] Zhang B, Chu GX, Wei CZ, Ye J, Li ZQ, Liang YC. 2011. The growth and antioxidant defense responses of wheat seedlings to omethoate stress. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 100: 273-279 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.719)
[4] Su YH, Liang YC. 2011. Transport via xylem of atrazine, 2,4-dinitrotoluene, and 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene in tomato and wheat seedlings. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology. 100: 284-288(影响因子:1.719)
[5] Song AL, Li P, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Nikolic M, Liang YC. 2011. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant and Soil. 344: 319-333. (通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[6] Li ZJ, Xie XY, Zhang SQ, Liang YC. 2011. Wheat growth and photosynthesis as affected by oxytetracycline as a soil contaminant. Pedosphere. 21(2): 244–250(通讯作者)
[7] Sun WC, Zhang J, Fan QH, Xue GF, Li ZJ, Liang YC 2010. Silicon-enhanced resistance to rice blast is attributed to silicon-mediated defence resistance and its role as physical barrier. European Journal of Plant Pathology. 128:39-49 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.931)
[8] Ge GF, Li ZJ, Fan FL, Chu GX, Hou ZA, Liang YC. 2010. Soil biological activity and their seasonal variations in response to long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Plant and Soil. 326:31–44(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[9] Liang YC, Zhu Y-G, Smith FA, Lambers H. 2010. Soil-plant interactions and sustainability of eco-agriculture in arid region: a crucially important topic to address. Plant and Soil. 326:1–2(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[10] Wakelin SA, Chu GX, Lardner R, Liang YC, McLaughlin MJ. 2009. A single application of Cu to field soil has long-term effects on bacterial community structure, diversity, and soil processes. Pedobiologia 53:149-158 (影响因子:2.414)
[11] Wakelin SA, Chu GX, Broos K, Clarke KR, Liang YC, McLaughlin MJ. 2010. Structural and functional response of soil microbiota across a Cu gradient are moderated by addition of plant substrate. Biology and Fertility of Soils 46:333-342 (影响因子:1.757)
[12] Song AL, Li ZJ, Zhang J, Xue GF, Fan FL, Liang YC. 2009. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 172:74-83 (通讯作者)(影响因子:4.144)
[13] Zhang J, Sun WC, Li ZJ, Liang YC, Song AL. 2009. Cadmium fate and tolerance in rice cultivars. Agronomy for Sustainable Development. 29: 483-490 (通讯作者)(影响因子:1.65)
[14] Chen WP, Hou ZA, Wu LS, Liang YC, Wei CZ. 2009. Effects of salinity and nitrogen on cotton growth in arid environment. Plant and Soil. 326:61–73(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.773)
[15] Guo B, Liang YC, Li ZJ and Han FX, 2009. Phosphorus adsorption and bio-availability in a paddy soil amended with pig manure compost and decaying rice straw. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis. 40: 2185-2199(通讯作者)(影响因子:0.357)
[16] Ma YB, Li JM, Li XY, Tang X, Liang YC, Huang SM, Wang BR, Liu H, Yang XY. 2009. Phosphorus accumulation and depletion in soils in wheat-maize cropping systems: modeling and validation. Field Crops Research. 110:207-212 (影响因子:2.336)
[17] Guo B, Liang YC, Zhu YG. 2009. Does salicylic acid regulate antioxidant defense system, cell death and cadmium uptake and partitioning to acquire cadmium tolerance in rice subjected to cadmium stress? Journal of Plant Physiology, 166: 20-31 (通讯作者)(影响因子:2.5)
[18] Su YH, Zhu YG and Liang YC. 2009. Interactions of mixed organic contaminants in uptake by rice seedlings, Chemosphere, 74: 890-895(通讯作者)(影响因子:3.253)
[19] Ge GF, Li ZJ, Zhang J, Wang LG, Xu MG, Zhang JB, Xie XL, Wang JK, Liang YC. 2009. Geographical and climatic differences in long-term effect of organic and inorganic amendments on soil enzymatic activities and respiration in field experimental stations of China. Ecological Complexity. 6: 421-431(通讯作者)(影响因子:2.03)
[20] Zhang J, Li ZJ, Ge GF, Liang YC, Wu LS. 2009. Impacts of soil organic matter, pH and exogenous copper on sorption behavior of norfloxacin in three soils. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 21: 632–640(通讯作者)(影响因子:1.414)
[21] Wang LG, Liang YC, Jiang X. 2008. Analysis of eight organophosphorus pesticide residues in fresh vegetables retailed in agricultural product markets of Nanjing, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81(4):377-382(影响因子:0.609)
免责声明:本网站所刊登的文章、图片版权均归原作者所有,不代表本公司观点,若有疑义,请与智库联系处理。
政商智库网隶属于北京正商方略经济咨询中心是一家独立的政策研究与咨询机构。广泛联络国内外政府领袖、经济学家、诺贝尔奖学者等,举办国际峰会论坛、组织技术交流、行业研讨会及参访,为社会各界提供智力支持。联系电话:13810102624(王老师)
主要业务领域有:战略咨询、公关服务、承接政府和企业委托、邀请专家出席论坛会议授课等。